Back to Access Cavities
MandibularOval
Mandibular First Premolar
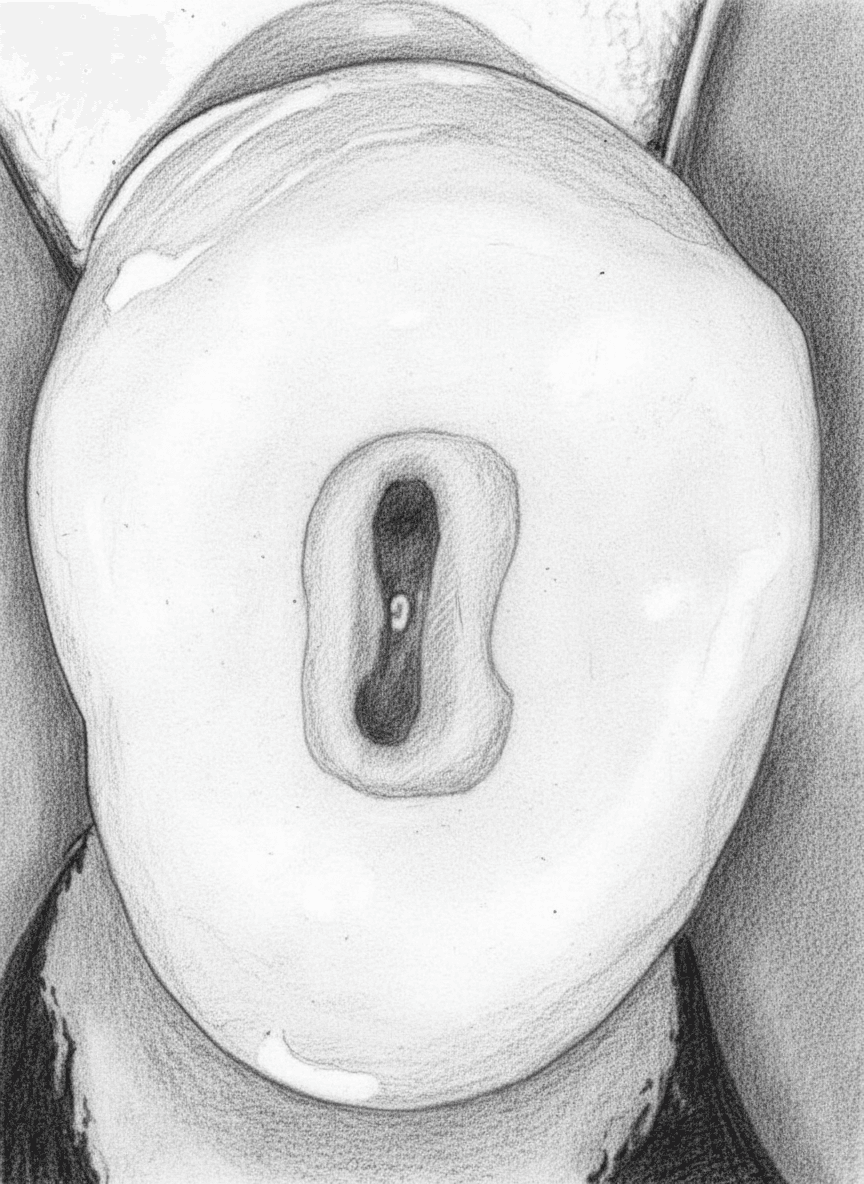
Mandibular First Premolar - Axial View showing oval access cavity
Average Length21.6 mm
Root Development13 years
Universal #21, 28
FDI #34, 44
Access Cavity Design
ShapeOval/Kidney
OrientationBuccolingual
Entry PointThrough occlusal surface, may require buccal cusp reduction
Canal Anatomy
Configurations
Single canal70-76%
Two canals18-24%
C-shaped canalUp to 67% with radicular groove
Canal Positions
MCMain Canal
May bifurcate in middle or apical third
BBuccal Canal
When 2 canals present
LLingual Canal
When 2 canals present
Danger Zones
- ⚠Lingual perforation - crown tilts lingually
- ⚠Counter by directing bur more buccally toward CEJ center
Clinical Tips
⚠️
Warning
HIGH lingual perforation risk - tooth crown tilts lingually, direct bur BUCCALLY
💡
Tip
Radicular groove on proximal surface = high probability of C-shaped anatomy
🔧
Technique
CBCT valuable for preoperative assessment in complex cases
⚠️
Warning
Bifurcation usually occurs in middle or apical third - not visible on radiograph
Anatomical Variations
C-Shaped Canal
Up to 67% with radicular grooveSingle fused root with C-shaped configuration
Access Modification: Oval to kidney-shaped access, requires thorough 3D cleaning