Back to Access Cavities
MandibularTrapezoidal
Mandibular Second Molar
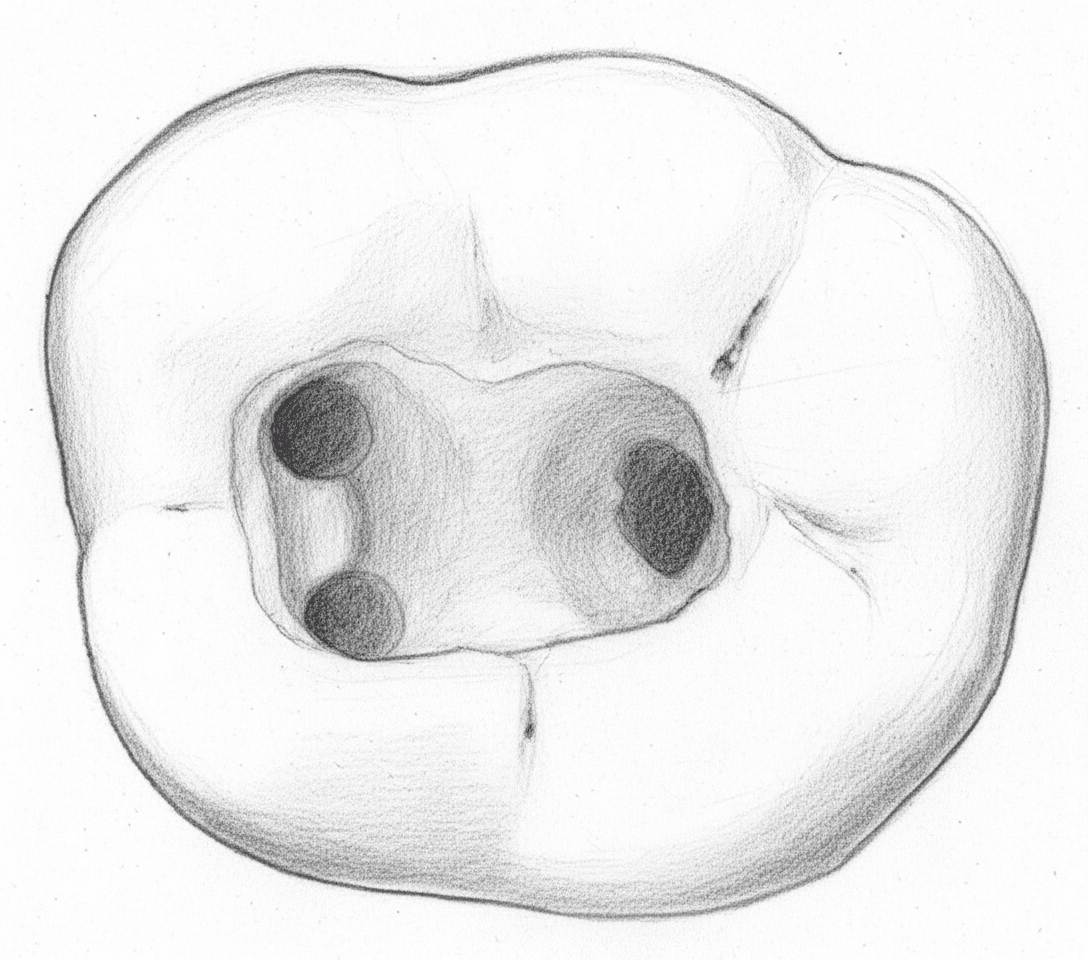
Mandibular Second Molar - Axial View showing trapezoidal access with canal orifices
Average Length19.8 mm
Root Development15 years
Universal #18, 31
FDI #37, 47
Access Cavity Design
ShapeTrapezoidal
OrientationSimilar to first molar but smaller
Entry PointMesial two-thirds of occlusal surface
Canal Anatomy
Configurations
2 roots, 3 canals~79%
2 roots, 2 canals~13%
C-shaped anatomy0.6-45.5% (ethnic)
Canal Positions
MBMesiobuccal
May appear as single oval with ML in fused roots
MLMesiolingual
May be fused with MB
DDistal
Typically single canal
CC-Shaped
Continuous ribbon-shaped orifice from MB to D
Danger Zones
- ⚠Thin lingual wall in C-shaped canals - HIGH perforation risk
Clinical Tips
⚠️
Warning
C-shaped canal prevalence: Up to 45% in Korean population
💡
Tip
C-shaped appearance: Ribbon-shaped orifice connecting MB to D (180° arch)
🔧
Technique
For C-shaped: Locate main canals first, then clean connecting isthmuses
⚠️
Warning
High perforation risk on thin lingual wall - use smaller taper files
🔧
Technique
Thermoplasticized GP mandatory for C-shaped obturation
Anatomical Variations
C-Shaped Canal
0.6-45.5%Single fused root with ribbon-shaped canal system
Access Modification: Expect continuous C-shaped or semicolon orifice, avoid over-extension
Ethnic Variation
Korean31.3-45.5%
Chinese0.6-41.27%
Burmese22.4%
Caucasian<5%