Back to Access Cavities
MaxillaryOvoid
Maxillary First Premolar
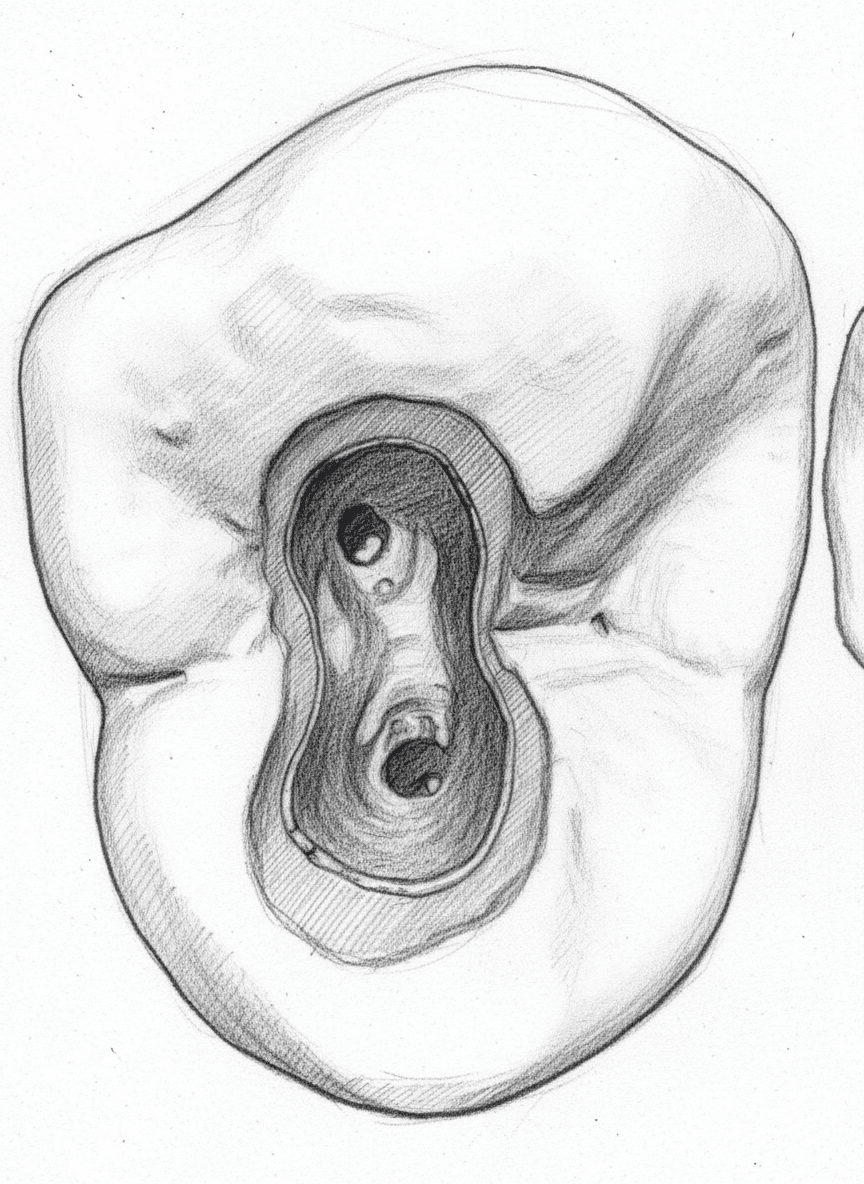
Maxillary First Premolar - Axial View showing ovoid access cavity with buccal and palatal canals
Average Length21.0 mm
Root Development13 years
Universal #5, 12
FDI #14, 24
Access Cavity Design
ShapeOvoid/T-Shaped
OrientationBuccopalatal
Entry PointCentral occlusal surface, middle of central sulcus
Landmarks
- Cusp tips define B-P extension
Do Not Invade
- Mesial marginal ridge
Canal Anatomy
Configurations
2 canals (buccal + palatal)75-90%
1 canal8-18%
3 canals (MB + DB + P)1-6%
Canal Positions
BBuccal Canal
Directly beneath buccal cusp tip
PPalatal Canal
Directly beneath palatal cusp tip
MBMesiobuccal Canal
When 3 canals present
DBDistobuccal Canal
When 3 canals present
Danger Zones
- ⚠Mesial concavity (furcation groove) - dentin often <1 mm thick
- ⚠Strip perforation risk 4-6 mm below orifice
Clinical Tips
🔧
Technique
Sieraski's Rule: Mid-root M-D width ≥ crown width suggests 3 canals
🔧
Technique
Take 2-3 angled radiographs (SLOB rule) to detect additional canals
🔧
Technique
NaOCl bubble test can reveal hidden orifices
⚠️
Warning
Do NOT over-enlarge narrow buccal canals - roots are slender
🔧
Technique
Use anti-curvature filing toward thicker (distal/palatal) wall